Import from GitHub
If you already have an application that you would like to bring into Diploi, you can import it using GitHub.
How to Import an Existing App into Diploi
Diploi offers two ways to import projects, by selecting the repo you want to import from a list of available repositories in your GitHub account or by using a URL.
-
Start a new project

-
Then switch from “Start From Scratch” to the “Import Repository” tab

-
Now you can select the source code you want to import. You can either select a repository stored in your own GitHub account or use a URL to import a public repo.
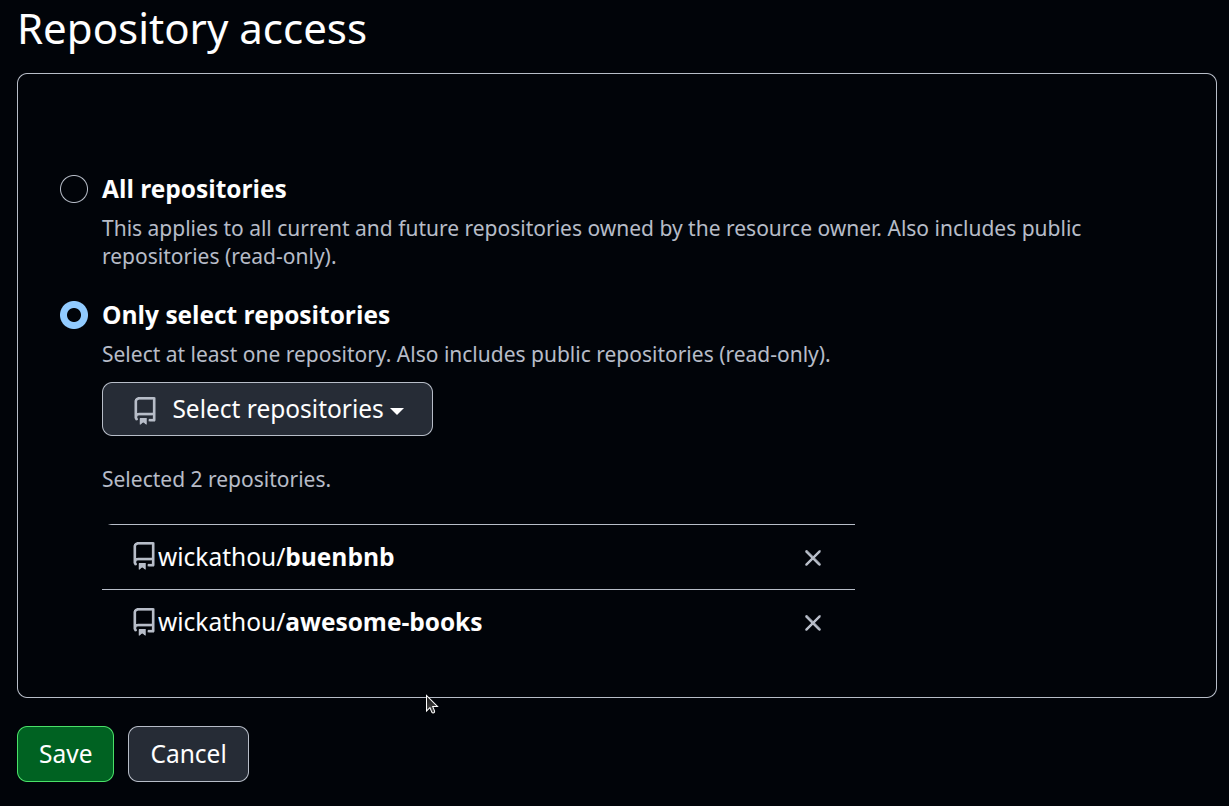
-
Once you have selected the repository you’ll import, click on the “Analyze Repository” button. Diploi will then look for the configuration files in your repository, for example,
package.jsonor ‘requirements.txt’, to determine how to properly import your project to Diploi.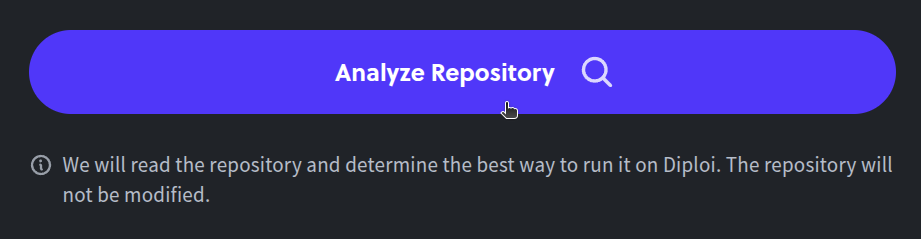
-
After Diploi analyzes your repository, you’ll be able to make some adjustments to the project before launching on Diploi. Once your project is set up, just click on “Launch Stack” to start your first deployment.
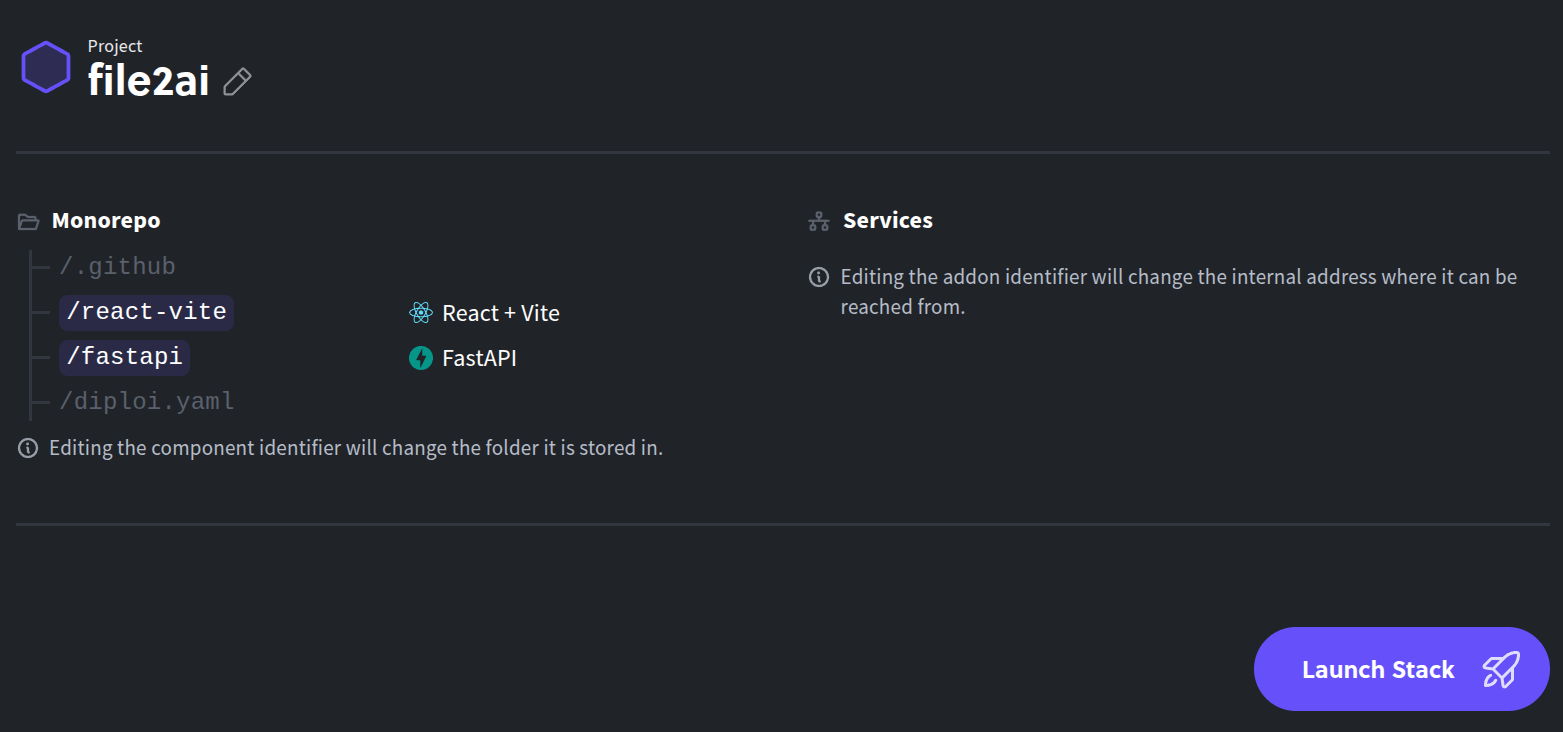
-
Now you should have a development deployment running. If your project is not loading properly or fails to start, check the deployment logs.
Other considerations
Run command config
By default, Diploi will use common run commands for development and staging/production deployments, so there might be some situations when your imported application might fail because your project uses different run commands. To handle these situations, you can either modify the Dockerfile and Dockerfile.dev created by diploi, or modify your app’s config to include the commands used by Diploi to run your application.
Importing an external public repository
When you can import a publicly available repository, which doesn’t belong to your GitHub account, you will have the option of creating a new repository in your account to store your code or start a project without a repository.
In case you choose to proceed without a repo, your project won’t be able to start a Production or Staging deployment, because Diploi creates a GitHub Action which takes care of creating a build of your project, which can be ran in Staging and Production.
Importing an app from a repository you own
When you import from a repo you own, Diploi will use the same repository by default to store your code, so any changes you make to your project can be pushed to the same repository you imported from.
Currently, you can’t import a repository and save it in a new repository.
Supported Applications
Although it is technically possible to import any application, not every app will work right away, and they might require additional work in order to run properly after you import them to Diploi.
You can import any application built with Diploi, or with any of these frameworks:
Apps built on Diploi
Any application built on Diploi can be imported into a new project without any additional configuration. Diploi will provision any component and add-on specified in the diploi.yaml file, but with the caveat that any environment variables used in the project must then be set manually, since Diploi doesn’t store the project’s secrets on GitHub.
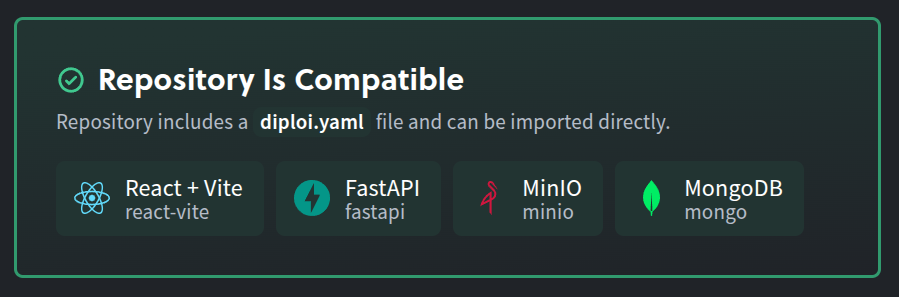
Apps built on Lovable
If you built a project on Lovable, you can seamlessly import it to Diploi. All you need to do is sync your application on GitHub.
For Lovable projects using Supabase, you can use the open-source version of Supabase that is available on Diploi. You can add Supabase by adding the snippet to your diploi.yaml file.
- name: Supabase identifier: supabase package: https://github.com/diploi/component-supabase#mainPaste the snippet within the components field in the diploi.yaml, usually found in the root of your project.
components: - name: Lovable ...
- name: Supabase identifier: supabase package: https://github.com/diploi/component-supabase#mainIf you would like a detailed walkthrough about how to import an application built with Lovable, click here to check our tutorial explaining how to do it. We also have a guide walkthrough explaining how to use Cursor for your imported Lovable app, which you can check by clicking here.
Running Supabase Migrations after Importing a Lovable App
If you are using the Lovable project with Supabase, you’ll need to run the necessary migrations, which should be stored inside your Supabase folder, as migrations.
You can apply the migrations to your new Supabase instance by running the command supabase migration up from the development environment created when you import the project.
Apps built with Node.js or React + Vite
Diploi allows you to import any application built with Node or React-Vite, but it might require changes if you expose non-default ports for your application or run if your application uses special commands to run in development, staging, or staging/production.
Default Config for Imported apps
These are the default values used by Diploi to run applications. If your import app uses different commands from the ones shown here, make sure to either add or modify them in your project to match these values, or you can also modify these defaults by editing the Dockerfiles created by Diploi inside of your project.
- Port exposed: 3000
- Package manager: npm
- Development
- Package installation command:
npm install - RUN command:
npm run dev
- Package installation command:
- Staging
- Package installation command:
npm install - Build command:
npm run build - RUN command:
npm run start
- Package installation command:
- Production
- Package installation command:
npm install - RUN command:
npm run start
- Package installation command:
- Port exposed: 5173
- Package manager: npm
- Development
- Package installation command:
npm install - RUN command:
npm run dev
- Package installation command:
- Staging
- Package installation command:
npm install - Build command:
npm run build - RUN command:
npm run start
- Package installation command:
- Production
- Package installation command:
npm install - RUN command:
npm run start
- Package installation command: